##4.中断下半部
软中断数据结构:
include/linux/interrupt.h:
/* softirq mask and active fields moved to irq_cpustat_t in
* asm/hardirq.h to get better cache usage. KAO
*/
struct softirq_action
{
void (*action)(struct softirq_action *);
};
include/linux/softirq.c:
static struct softirq_action softirq_vec[NR_SOFTIRQS] __cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
软中断的优先级是该数组的下标
enum
{
HI_SOFTIRQ=0,
TIMER_SOFTIRQ,
NET_TX_SOFTIRQ,
NET_RX_SOFTIRQ,
BLOCK_SOFTIRQ,
BLOCK_IOPOLL_SOFTIRQ,
TASKLET_SOFTIRQ,
SCHED_SOFTIRQ,
HRTIMER_SOFTIRQ,
RCU_SOFTIRQ, /* Preferable RCU should always be the last softirq */
NR_SOFTIRQS
};
###4.1软中断
###4.1.1内核上下文标识

内核通过thread_info中的preempt_count来标识各种中断上下文 通过add_preempt_count(x),x代表各个mask偏移量,来设置相应的偏移量置位
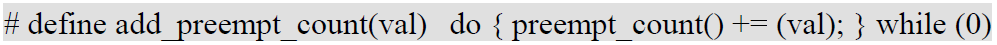
###4.1.1.1硬件中断,HARDIRQ_OFFSET的标识
我们知道当硬件来中断的时候内核的流程为最终调用asm_do_IRQ→handle_IRQ
在这个handle_IRQ函数里,入口和出口分别为函数irq_enter(),irq_exit()
arch/arm/kernel/irq.c
/*
* handle_IRQ handles all hardware IRQ's. Decoded IRQs should
* not come via this function. Instead, they should provide their
* own 'handler'. Used by platform code implementing C-based 1st
* level decoding.
*/
void handle_IRQ(unsigned int irq, struct pt_regs *regs)
{
struct pt_regs *old_regs = set_irq_regs(regs);
irq_enter(); ///
/*
* Some hardware gives randomly wrong interrupts. Rather
* than crashing, do something sensible.
*/
if (unlikely(irq >= nr_irqs)) {
if (printk_ratelimit())
printk(KERN_WARNING "Bad IRQ%u\n", irq);
ack_bad_irq(irq);
} else {
generic_handle_irq(irq);
}
/* AT91 specific workaround */
irq_finish(irq);
irq_exit(); ///
set_irq_regs(old_regs);
}
/*
* asm_do_IRQ is the interface to be used from assembly code.
*/
asmlinkage void __exception_irq_entry
asm_do_IRQ(unsigned int irq, struct pt_regs *regs)
{
handle_IRQ(irq, regs);
}
/*
* Enter an interrupt context.
*/
void irq_enter(void)
{
int cpu = smp_processor_id();
rcu_irq_enter();
if (is_idle_task(current) && !in_interrupt()) {
/*
* Prevent raise_softirq from needlessly waking up ksoftirqd
* here, as softirq will be serviced on return from interrupt.
*/
local_bh_disable();
tick_check_idle(cpu);
_local_bh_enable();
}
__irq_enter();
}
/*
* It is safe to do non-atomic ops on ->hardirq_context,
* because NMI handlers may not preempt and the ops are
* always balanced, so the interrupted value of ->hardirq_context
* will always be restored.
*/
#define __irq_enter() \
do { \
account_system_vtime(current); \
add_preempt_count(HARDIRQ_OFFSET); \ 这行代码正是将hardirq对应的bit增加1,标识内核此时正处于中断上下文之中。
trace_hardirq_enter(); \
} while (0)
/*
* Exit an interrupt context. Process softirqs if needed and possible:
*/
void irq_exit(void)
{
account_system_vtime(current);
trace_hardirq_exit();
sub_preempt_count(IRQ_EXIT_OFFSET);
if (!in_interrupt() && local_softirq_pending())
invoke_softirq();
#ifdef CONFIG_NO_HZ
/* Make sure that timer wheel updates are propagated */
if (idle_cpu(smp_processor_id()) && !in_interrupt() && !need_resched())
tick_nohz_irq_exit();
#endif
rcu_irq_exit();
sched_preempt_enable_no_resched();
}
在irq_exit()函数中,我们看到了调用了invoke_softirq()用来处理所有处于pending状态的软中断。该函数的执行条件为:!in_interrupt() && local_softirq_pending(),in_interrupt()我们已经从上下文中研究过是判断此处是否处于硬件中断和软件中断上下文中,如果处于两个上下文之一,那么就不会执行软中断。local_softirq_pending()是软中断pending位图变量__softirq_pending对应的软中断bit位被置位,代表的是将对应的软中断设置为可执行。
分析invoke_softirq()函数:
static inline void invoke_softirq(void)
{
if (!force_irqthreads) {
#ifdef __ARCH_IRQ_EXIT_IRQS_DISABLED //这里被定义为1
__do_softirq();
#else
do_softirq();
#endif
} else {
__local_bh_disable((unsigned long)__builtin_return_address(0),
SOFTIRQ_OFFSET);
wakeup_softirqd();
__local_bh_enable(SOFTIRQ_OFFSET);
}
}
__do_softirq与do_softirq我们将在下个章节具体讲解。
###4.1.1.2软件中断,SOFTIRQ_OFFSET的标识
kernel/softirq.c:
void local_bh_disable(void)
{
__local_bh_disable((unsigned long)__builtin_return_address(0),
SOFTIRQ_DISABLE_OFFSET);
}
static inline void __local_bh_disable(unsigned long ip, unsigned int cnt)
{
add_preempt_count(cnt);
barrier();
}
static void __local_bh_enable(unsigned int cnt)
{
WARN_ON_ONCE(in_irq());
WARN_ON_ONCE(!irqs_disabled());
if (softirq_count() == cnt)
trace_softirqs_on((unsigned long)__builtin_return_address(0));
sub_preempt_count(cnt);
}
/*
* Special-case - softirqs can safely be enabled in
* cond_resched_softirq(), or by __do_softirq(),
* without processing still-pending softirqs:
*/
void _local_bh_enable(void)
{
__local_bh_enable(SOFTIRQ_DISABLE_OFFSET);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(_local_bh_enable);
static inline void _local_bh_enable_ip(unsigned long ip)
{
WARN_ON_ONCE(in_irq() || irqs_disabled());
#ifdef CONFIG_TRACE_IRQFLAGS
local_irq_disable();
#endif
/*
* Are softirqs going to be turned on now:
*/
if (softirq_count() == SOFTIRQ_DISABLE_OFFSET)
trace_softirqs_on(ip);
/*
* Keep preemption disabled until we are done with
* softirq processing:
*/
sub_preempt_count(SOFTIRQ_DISABLE_OFFSET - 1);
if (unlikely(!in_interrupt() && local_softirq_pending()))
do_softirq();
dec_preempt_count();
#ifdef CONFIG_TRACE_IRQFLAGS
local_irq_enable();
#endif
preempt_check_resched();
}
void local_bh_enable(void)
{
_local_bh_enable_ip((unsigned long)__builtin_return_address(0));
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(local_bh_enable);
###4.1.2软中断处理函数do_softirq
asmlinkage void do_softirq(void)
{
__u32 pending;
unsigned long flags;
if (in_interrupt())
return;
注释:此处要求软中断不能发生在任何硬件和软件中断上下文中。
local_irq_save(flags);
pending = local_softirq_pending();
注释:确定当前CPU软中断位图中所有置位的比特位,注意此过程必须在关闭本地中断前提下,防止其他进程对该位图做修改。local_irq_save(flags);在这里就是最好的解释。
if (pending)
__do_softirq();
local_irq_restore(flags);
}
/*
* We restart softirq processing MAX_SOFTIRQ_RESTART times,
* and we fall back to softirqd after that.
*
* This number has been established via experimentation.
* The two things to balance is latency against fairness -
* we want to handle softirqs as soon as possible, but they
* should not be able to lock up the box.
*/
#define MAX_SOFTIRQ_RESTART 10
asmlinkage void __do_softirq(void)
{
struct softirq_action *h;
__u32 pending;
int max_restart = MAX_SOFTIRQ_RESTART;
int cpu;
pending = local_softirq_pending();
注释:确定当前CPU软中断位图中所有置位的比特位
account_system_vtime(current);
__local_bh_disable((unsigned long)__builtin_return_address(0),
SOFTIRQ_OFFSET);
lockdep_softirq_enter();
cpu = smp_processor_id();
restart:
/* Reset the pending bitmask before enabling irqs */
set_softirq_pending(0);
注释:清除pending位图标志,注意从此处的代码向上都需要在关本地中断的情况下执行,为了避免pending标志被别的进程修改。
local_irq_enable();
注释:注意,软中断处理函数的执行期间是允许外部硬件中断的。
h = softirq_vec;
do {
if (pending & 1) {
unsigned int vec_nr = h - softirq_vec;
int prev_count = preempt_count();
kstat_incr_softirqs_this_cpu(vec_nr);
trace_softirq_entry(vec_nr);
h->action(h);
注释:真正的软中断处理函数
trace_softirq_exit(vec_nr);
if (unlikely(prev_count != preempt_count())) {
printk(KERN_ERR "huh, entered softirq %u %s %p"
"with preempt_count %08x,"
" exited with %08x?\n", vec_nr,
softirq_to_name[vec_nr], h->action,
prev_count, preempt_count());
preempt_count() = prev_count;
}
rcu_bh_qs(cpu);
}
h++;
pending >>= 1;
} while (pending);
local_irq_disable();
注释:中断处理完成后,我们需要重新检查是否在,软中断期间,pending位又被修改
pending = local_softirq_pending();
if (pending && --max_restart)
goto restart;
if (pending)
wakeup_softirqd();
lockdep_softirq_exit();
account_system_vtime(current);
__local_bh_enable(SOFTIRQ_OFFSET);
}
###4.1.3软中断的使用
###4.1.3.1注册软中断
open_softirq函数负责注册软中断处理函数
void open_softirq(int nr, void (*action)(struct softirq_action *))
{
softirq_vec[nr].action = action;
}
Linux中tasklet为例子: main.c中的start_kernel中有调用:
void __init softirq_init(void)
{
int cpu;
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) {
int i;
per_cpu(tasklet_vec, cpu).tail =
&per_cpu(tasklet_vec, cpu).head;
per_cpu(tasklet_hi_vec, cpu).tail =
&per_cpu(tasklet_hi_vec, cpu).head;
for (i = 0; i < NR_SOFTIRQS; i++)
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&per_cpu(softirq_work_list[i], cpu));
}
register_hotcpu_notifier(&remote_softirq_cpu_notifier);
open_softirq(TASKLET_SOFTIRQ, tasklet_action);
open_softirq(HI_SOFTIRQ, tasklet_hi_action);
}
###4.1.3.2触发软中断
通过raise_softirq将软中断设置为挂起状态,参数为软中断号。
raise_softirq_irqoff作用是在触发软中断前关闭中断,触发后恢复中断状态。
Tasklet为例子:
include/linux/interrupt.h:
static inline void tasklet_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{
if (!test_and_set_bit(TASKLET_STATE_SCHED, &t->state))
__tasklet_schedule(t);
}
void __tasklet_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{
unsigned long flags;
local_irq_save(flags);
t->next = NULL;
*__this_cpu_read(tasklet_vec.tail) = t;
__this_cpu_write(tasklet_vec.tail, &(t->next));
raise_softirq_irqoff(TASKLET_SOFTIRQ);
local_irq_restore(flags);
}
###4.1.3.3激活软中断
asmlinkage void __do_softirq(void)
{
struct softirq_action *h;
__u32 pending;
int max_restart = MAX_SOFTIRQ_RESTART;
int cpu;
pending = local_softirq_pending();
account_system_vtime(current);
__local_bh_disable((unsigned long)__builtin_return_address(0),
SOFTIRQ_OFFSET);
lockdep_softirq_enter();
cpu = smp_processor_id();
restart:
/* Reset the pending bitmask before enabling irqs */
set_softirq_pending(0);
local_irq_enable();
h = softirq_vec;
do {
if (pending & 1) {
unsigned int vec_nr = h - softirq_vec;
int prev_count = preempt_count();
kstat_incr_softirqs_this_cpu(vec_nr);
trace_softirq_entry(vec_nr);
h->action(h); //最终调用open_softirq时候注册的tasklet_action(仅以tasklet为例子)
trace_softirq_exit(vec_nr);
if (unlikely(prev_count != preempt_count())) {
printk(KERN_ERR "huh, entered softirq %u %s %p"
"with preempt_count %08x,"
" exited with %08x?\n", vec_nr,
softirq_to_name[vec_nr], h->action,
prev_count, preempt_count());
preempt_count() = prev_count;
}
rcu_bh_qs(cpu);
}
h++;
pending >>= 1;
} while (pending);
local_irq_disable();
pending = local_softirq_pending();
if (pending && --max_restart)
goto restart;
if (pending)
wakeup_softirqd();
lockdep_softirq_exit();
account_system_vtime(current);
__local_bh_enable(SOFTIRQ_OFFSET);
}
static void tasklet_action(struct softirq_action *a)
{
struct tasklet_struct *list;
local_irq_disable();
list = __this_cpu_read(tasklet_vec.head);
__this_cpu_write(tasklet_vec.head, NULL);
__this_cpu_write(tasklet_vec.tail, &__get_cpu_var(tasklet_vec).head);
local_irq_enable();
while (list) {
struct tasklet_struct *t = list;
list = list->next;
if (tasklet_trylock(t)) {
注释:tasklet_trylock用于禁用已经被调度的tasklet,在多CPU的系统中。
if (!atomic_read(&t->count)) {
if (!test_and_clear_bit(TASKLET_STATE_SCHED, &t->state))
BUG();
t->func(t->data); //
tasklet_init中初始化好了的func和data,才是真正要执行的函数。
使用方法:
tasklet_init(&ttime->tasklet, __tasklet_hrtimer_trampoline, (unsigned long)ttimer);
原型:
void tasklet_init(struct tasklet_struct *t,
void (*func)(unsigned long), unsigned long data)
{
t->next = NULL;
t->state = 0;
atomic_set(&t->count, 0);
t->func = func;
t->data = data;
}
tasklet_unlock(t);
continue;
}
tasklet_unlock(t);
}
local_irq_disable();
t->next = NULL;
*__this_cpu_read(tasklet_vec.tail) = t;
__this_cpu_write(tasklet_vec.tail, &(t->next));
__raise_softirq_irqoff(TASKLET_SOFTIRQ);
local_irq_enable();
}
}
tasklet_trylock原型:
static inline int tasklet_trylock(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{
return !test_and_set_bit(TASKLET_STATE_RUN, &(t)->state);
}
###4.1.4软中断调用时机
前提:
软中断真正的开始执行使用:do_softirq(),__do_softirq()
软中断被设置可以执行使用:raise_softirq(),raise_softirq_irqoff()
软中断只有在设置可执行位置位后才能开始执行。
谁调用了do_softirq(),__do_softirq()?
- 每一个中断上下文中的irq_exit()函数中
- 软中断守护进程:run_ksoftirqd()函数中
raise_softirq(),raise_softirq_irqoff()做了些什么?
/*
* This function must run with irqs disabled!
*/
inline void raise_softirq_irqoff(unsigned int nr)
{
__raise_softirq_irqoff(nr);
设置pending位置位,需要设置软中断可运行标志
/*
* If we're in an interrupt or softirq, we're done
* (this also catches softirq-disabled code). We will
* actually run the softirq once we return from
* the irq or softirq.
*
* Otherwise we wake up ksoftirqd to make sure we
* schedule the softirq soon.
*/
if (!in_interrupt())
wakeup_softirqd();
如果此时处于硬件或者软件中断上下文中,我们知道此时必将马上运行此软中断,因为如果是处于硬件上下文中的时候,马上就会在irq_exit中call软中断;如果此时处于软中断中,那么当执行的软中断执行完毕之后,软件会重新查看pending位,这个时候就可以执行上面的这个软中断。
}
总结:软中断调用的时机在每一次中断来之后的irq_exit函数中,执行了max_restart次软中断后,如果还有没有执行完的软中断处于pending状态中,那么我们就调用软中断守护程序run_ksoftirqd()来执行后面没有完成的软中断。
###4.2 Tasklet的使用
tasklet_struct数据结构:(include/linux/interrupt.h)
struct tasklet_struct
{
struct tasklet_struct *next;
unsigned long state;
atomic_t count;
void (*func)(unsigned long);
unsigned long data;
};
一个使用的例子:
static struct tasklet_struct my_tasklet; /*定义自己的tasklet_struct变量*/
static void tasklet_handler (unsigned long data)
{
printk(KERN_ALERT "tasklet_handler is running.\n");
}
static int __init test_init (void)
{
tasklet_init(&my_tasklet, tasklet_handler, 0); /*挂入钩子函数tasklet_handler*/
tasklet_schedule(&my_tasklet); /*触发softirq的TASKLET_SOFTIRQ,在下一次运行softirq时运行这个tasklet*/
return 0;
}
static void __exit test_exit(void)
{
tasklet_kill(&my_tasklet); /*禁止该tasklet的运行*/
printk(KERN_ALERT "test_exit running.\n");
}
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
module_init(test_init);
module_exit(test_exit);
###4.2.1初始tasklet
动态创建tasklet:
tasklet_init(&my_tasklet, tasklet_handler, 0);
tasklet_handler,tasklet的处理程序,需要满足:
- 不能睡眠
- 允许响应中断,做好与中断处理程序的同步
- 相同的tasklet绝不会同时执行
- 不同的tasklet之间或者软中断之间的同步
void tasklet_init(struct tasklet_struct *t,
void (*func)(unsigned long), unsigned long data)
{
t->next = NULL;
t->state = 0;
atomic_set(&t->count, 0);
t->func = func;
t->data = data;
}
###4.2.2调度tasklet
static inline void tasklet_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{
if (!test_and_set_bit(TASKLET_STATE_SCHED, &t->state))
__tasklet_schedule(t);
}
void __tasklet_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{
unsigned long flags;
local_irq_save(flags);
t->next = NULL;
*__this_cpu_read(tasklet_vec.tail) = t;
__this_cpu_write(tasklet_vec.tail, &(t->next));
注释:将需要调度的tasklet_struct放入到tasklet_vec链表中。
raise_softirq_irqoff(TASKLET_SOFTIRQ);
local_irq_restore(flags);
}
void __tasklet_hi_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{
unsigned long flags;
local_irq_save(flags);
t->next = NULL;
*__this_cpu_read(tasklet_hi_vec.tail) = t;
__this_cpu_write(tasklet_hi_vec.tail, &(t->next));
注释:将需要调度的tasklet_struct放入到tasklet_hi_vec链表中,该tasklet的优先级比较高。
raise_softirq_irqoff(HI_SOFTIRQ);
local_irq_restore(flags);
}
###4.2.3 激活tasklet
参考《4.1软中断的使用》章节。
###4.2.4软中断和tasklet
软中断: 执行效率高 加锁严格
Tasklet: 接口简单 锁保护要求宽松 性能也不错
###4.3工作队列的使用
数据结构:
工作者线程的数据结构:
/*
* The externally visible workqueue abstraction is an array of
* per-CPU workqueues:
*/
struct workqueue_struct {
unsigned int flags; /* W: WQ_* flags */
union {
struct cpu_workqueue_struct __percpu *pcpu;
struct cpu_workqueue_struct *single;
unsigned long v;
} cpu_wq; /* I: cwq's */
struct list_head list; /* W: list of all workqueues */
struct mutex flush_mutex; /* protects wq flushing */
int work_color; /* F: current work color */
int flush_color; /* F: current flush color */
atomic_t nr_cwqs_to_flush; /* flush in progress */
struct wq_flusher *first_flusher; /* F: first flusher */
struct list_head flusher_queue; /* F: flush waiters */
struct list_head flusher_overflow; /* F: flush overflow list */
mayday_mask_t mayday_mask; /* cpus requesting rescue */
struct worker *rescuer; /* I: rescue worker */
int nr_drainers; /* W: drain in progress */
int saved_max_active; /* W: saved cwq max_active */
#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP
struct lockdep_map lockdep_map;
#endif
char name[]; /* I: workqueue name */
};
表示工作的数据结构:
struct work_struct {
atomic_long_t data;
struct list_head entry;
work_func_t func;
#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP
struct lockdep_map lockdep_map;
#endif
};
typedef void (*work_func_t)(struct work_struct *work);
###4.3.1工作队列初始化
用来初始化work_struct结构体
#define INIT_WORK(_work, _func) \
do { \
__INIT_WORK((_work), (_func), 0); \
} while (0)
#define __INIT_WORK(_work, _func, _onstack) \
do { \
__init_work((_work), _onstack); \
(_work)->data = (atomic_long_t) WORK_DATA_INIT(); \
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&(_work)->entry); \
PREPARE_WORK((_work), (_func)); \
} while (0)
#endif
/*
* initialize a work item's function pointer
*/
#define PREPARE_WORK(_work, _func) \
do { \
(_work)->func = (_func); \
} while (0)
举例子:
struct work_structwork;
static void work_handler(struct work_struct *work) {
printk(“hello!\n”);
}
INIT_WORK(&work, work_handler);
该work_handler的基本要求:
- 运行在进程的上下文中
- 允许中断
- 可以睡眠
- 工作队列和内核其他部分同步和进程上下文的同步一样
###4.3.2工作队列的调度
kernel/workqueue.c:
/**
* schedule_work - put work task in global workqueue
* @work: job to be done
*
* Returns zero if @work was already on the kernel-global workqueue and
* non-zero otherwise.
*
* This puts a job in the kernel-global workqueue if it was not already
* queued and leaves it in the same position on the kernel-global
* workqueue otherwise.
*/
int schedule_work(struct work_struct *work)
{
return queue_work(system_wq, work);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(schedule_work);
###4.3.3工作队列刷新
/**
* flush_delayed_work - wait for a dwork to finish executing the last queueing
* @dwork: the delayed work to flush
*
* Delayed timer is cancelled and the pending work is queued for
* immediate execution. Like flush_work(), this function only
* considers the last queueing instance of @dwork.
*
* RETURNS:
* %true if flush_work() waited for the work to finish execution,
* %false if it was already idle.
*/
bool flush_delayed_work(struct delayed_work *dwork)
{
if (del_timer_sync(&dwork->timer))
__queue_work(raw_smp_processor_id(),
get_work_cwq(&dwork->work)->wq, &dwork->work);
return flush_work(&dwork->work);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(flush_delayed_work);
###4.3.4工作队列API
Linux 2.6内核使用了不少工作队列来处理任务,他在使用上和tasklet最大的不同是工作队列的函数可以使用休眠,而tasklet的函数是不允许使用休眠的。
工作队列的使用又分两种情况,一种是利用系统共享的工作队列来增加自己的工作,这种情况处理函数不能消耗过多时间,这样会影响共享队列中其他任务的处理;别的一种是创建自己的工作队列并添加工作。
(一)利用系统共享的工作队列添加工作:
第一步:声明或编写一个工作处理函数 void my_func(); 第二步:创建一个工作结构体变量,并将处理函数和参数的入口地址赋给这个工作结构体变量 DECLARE_WORK(my_work, my_func, &data); //编译时创建名为my_work的结构体变量并把函数入口地址和参数地址赋给它; 假如不想要在编译时创建,就用DECLARE_WORK()创建并初始化工作结构体变量,也可以在程序运行时再用INIT_WORK()创建 struct work_struct my_work; //创建一个名为my_work的结构体变量,创建后才能使用INIT_WORK() INIT_WORK(&my_work, my_func, &data); //初始化已经创建的my_work,其实便是往这个结构体变量中添加处理函数入口地址和data的地址,通常在驱动的open函数中完成
第三步:将工作结构体变量添加入系统的共享工作队列 schedule_work(&my_work); //添加入队列的工作完成后会自动从队列中删除 或 schedule_delayed_work(&my_work, tick); //延时tick个滴答后再提交工作
(二)创建自己的工作队列来添加工作
第一步:声明工作处理函数和一个指向工作队列的指针 void my_func(); struct workqueue_struct *p_queue;
第二步:创建自己的工作队列和工作结构体变量(通常在open函数中完成) p_queue = create_workqueue(“my_queue”); //创建一个名为my_queue的工作队列并把工作队列的入口地址赋给声明的指针
struct work_struct my_work; INIT_WORK(&my_work, my_func, &data); //创建一个工作结构体并初始化,和第一种情况的办法一样
第三步:将工作添加入自己创建的工作队列等待执行 queue_work(p_queue, my_work); //作用与schedule_work()相似,不同的是将工作添加入p_queue指针指向的工作队列而不是系统共享的工作队列
第四步:删除自己的工作队列 destory_workqueue(p_queue); //基本是在close函数中删除
总结:
首选tasklet,对于时间要求严格(time-critical),可使用softirq Tasklet、内核定时器都是使用softirq(软中断)实现
如果想运行在内核线程,进程上下文,可休眠,使用工作队列
In short, normal driver writers have two choices. First, do you need a schedulable entity to perform your deferred work—fundamentally, do you need to sleep for any reason? Then work queues are your only option. Otherwise, tasklets are preferred. Only if scalability becomes a concern do you investigate softirqs.
